STDs
Chlamydia
A frequent STD that can infect both men and women is chlamydia. It may harm a woman’s reproductive system permanently. Later pregnancy may become challenging or impossible as a result.
Gonorrhea
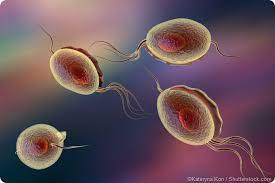
An STD called gonorrhea can infect the genitalia, rectum, and throat. It is fairly typical, particularly among young people between the ages of 15 and 24.
Syphilis
The symptoms of syphilis change as it progresses through different stages.
A mild irritation on the genitalia, rectum, or mouth characterizes the initial stage. The second stage is distinguished by a rash and occurs after the original sore has healed.
Hep B
The main way that this illness is communicated is through contact with infected bodily fluids. The symptoms might vary and include eye yellowing, stomach ache, and dark urine. Some people don’t show any symptoms, especially young children.
Hep C
The virus is transmitted through blood contact, such as that caused by sharing needles or using unsterile tattoo supplies.
Most folks don’t exhibit any symptoms. Those who do experience symptoms may include weariness, nauseousness, appetite loss, and skin and eye yellowing.
Mycoplasma
Like the other members of the class Mollicutes, the genus of bacteria known as Mycoplasma lacks a cell wall to protect its cell membranes. There is no peptidoglycan. Because of this trait, they are inherently resistant to drugs that interfere with cell wall formation.
Trichomoniasis
A parasitic infection that is spread through sexual contact.
One of the most prevalent sexually transmitted illnesses is trichoniasis. Multiple sexual partners and not using condoms during sex are risk factors.
A frequent STD that can infect both men and women is chlamydia. It may harm a woman’s reproductive system permanently. Later pregnancy may become challenging or impossible as a result.
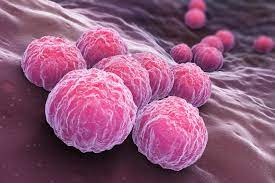
When you engage in vaginal, anal, or oral intercourse with someone who has syphilis, the infection is transferred sexually. It’s caused by bacteria. Syphilis is treated with antibiotic treatment. Syphilis, if left untreated, can cause blindness as well as harm to the brain, heart, eyes, and neurological system.

The clap, often known as gonorrhea, is a sexually transmitted disease (STI). Gonorrhea frequently has no symptoms, especially in those who were given the gender of a girl at birth. Your reproductive system determines the symptoms that are present. If you believe you have an infection, consult a healthcare professional. Antibiotics used quickly can help prevent long-term issues.
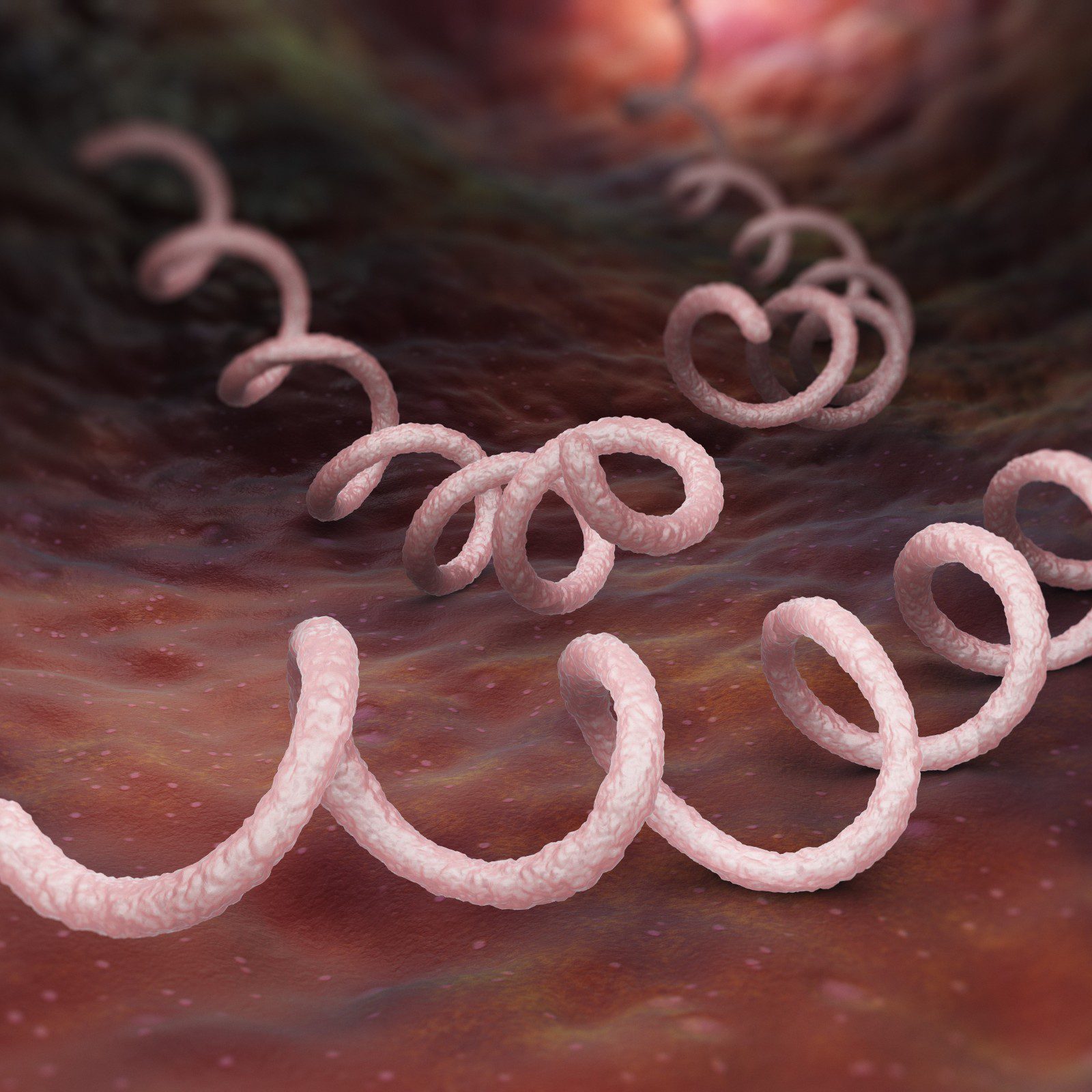
Your liver is impacted by the viral infection known as hepatitis B. The term “hepatitis” refers to an inflammation of the liver tissues. It starts out as an acute infection that is often mild. However, it can develop into a persistent infection in some people that never goes away.
Your liver suffers substantial long-term harm from chronic inflammation. Cirrhosis and liver failure may result from it. Hepatitis B infection, like other chronic liver illnesses, can harm the liver in this way without showing any symptoms. Many individuals are sick but are unaware of it.
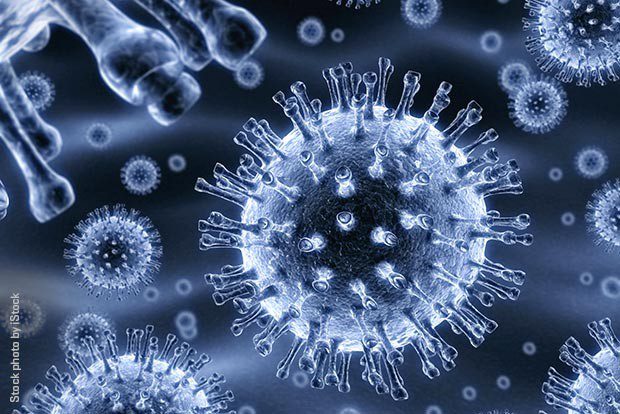
Your liver is impacted by the viral infection known as hepatitis C. It results in swelling and inflammation, which over time damages the tissues of your liver. The term “hepatitis” refers to liver inflammation. Hepatitis has a variety of causes, some of which are viruses. But hepatitis C is considerably more likely to persist in your body for a long period than other viral hepatitis causes.
Your liver suffers substantial damage over a long period of time from chronic inflammation. Hepatitis C is really one of the main reasons for liver failure and liver transplantation in the US. Most people are unable to detect liver inflammation. They don’t exhibit symptoms until after significant harm has been done.
Infections are brought on by the bacterium known as mycoplasma. There are many mycoplasma species that specifically target the respiratory, urinary, and vaginal systems as well as other parts of the body.
Since mycoplasmas lack cell walls, they are unusual. The majority of bacteria have cell walls, and certain antibiotics target cell walls to kill germs and improve your health. These antibiotics don’t act on mycoplasma since they don’t have cell walls.

The most prevalent treatable STD is trichomoniasis (also known as trich). Trich is an STD that can be treated with antibiotic medication. Most persons with trich don’t exhibit any symptoms, yet it is extremely common.
Each year, millions of people develop trichiasis. The parasite that causes it spreads incredibly quickly during sexual activity. Semen, pre-cum, and vaginal secretions are some examples of sexual fluids that contain the parasite.